STEP 10: Network Adjustments
If there is no Project Tracking ID (issued by NGS or set to 0000) associated with the project, perform network adjustments on all selected sessions. Typically, CORSs are held fixed in 3D while any vertical user marks with known or published orthometric heights may be constrained vertically at those heights. For additional information see Section 12, Network Adjustments.
If a Project Tracking ID was used, then the next step is a series of five sequential network adjustments (as shown in Fig. 12). After each step, carefully review the results and particularly the shifts in the coordinates. You may have to go back and reject some observations (or remove some constraints) and reprocess some sessions.
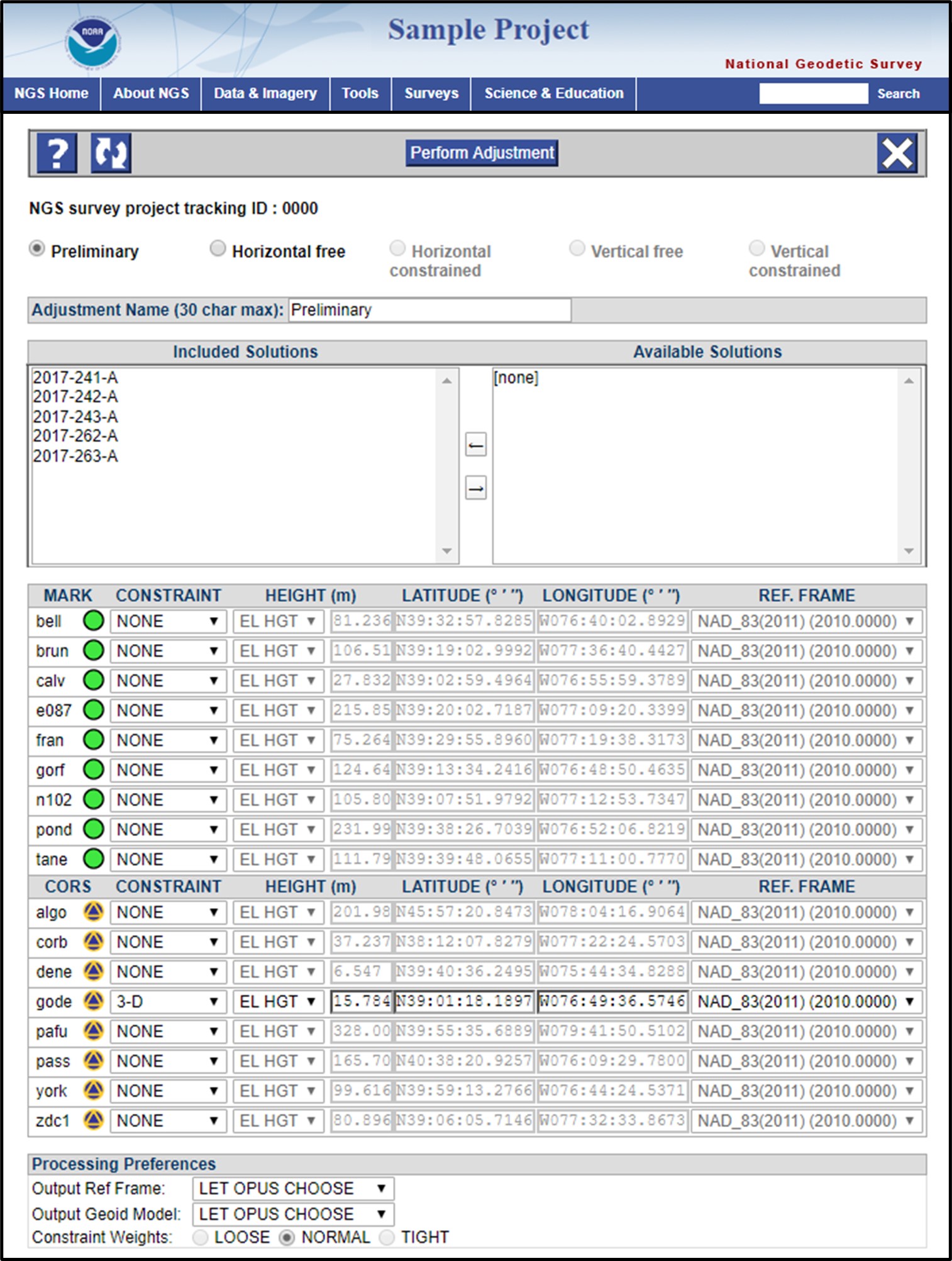
Fig. 12 Network adjustment window showing sequence of five network adjustments when a NGS Tracking ID is used.
Preliminary network adjustment: constrain the hub(s) (3D) and float all other stations. Make sure you have at least two good occupations (>2 hrs) per user mark.
Horizontal free network adjustment (minimally constrained - same design as the Preliminary): constrain only one station (3D), typically a hub. Analyze residuals, make sure they are small. If you have uploaded GVX vectors into your project, you are able to add them to your horizontal free network adjustment by selecting them in the available solutions section. See Section 12 for details on the horizontal free adjustment when including GVX vectors.
Horizontal constrained network adjustment: constrain all CORSs (3D) except the distant CORS. Constrain the (published) adjusted horizontal coordinates for all observed user marks with published lat/lons. Evaluate the coordinate shifts for the signs of any outliers. Evaluate the F-test result (see Section 12 for more guidance on applying the F-test).
Vertical free network adjustment (minimally constrained): constrain one hub in 2D; constrain to one (published) adjusted orthometric height (1D). Analyze residuals, make sure they are small.
Vertical constrained network adjustment: constrain one hub (2D), float all other CORSs. Constrain all user marks that have published, adjusted orthometric heights. Evaluate the vertical shifts as well as the results of the F-test.