11.2. Selecting the Session Network Design
The Network Design selection is identified at the bottom of the session processing page, and the expression of the design can be seen in the table listing the marks and CORSs (which are used as hubs, and which are constrained). There are three options available: “USER”, “CORS”, and “MST”, as shown in Fig. 11.3.
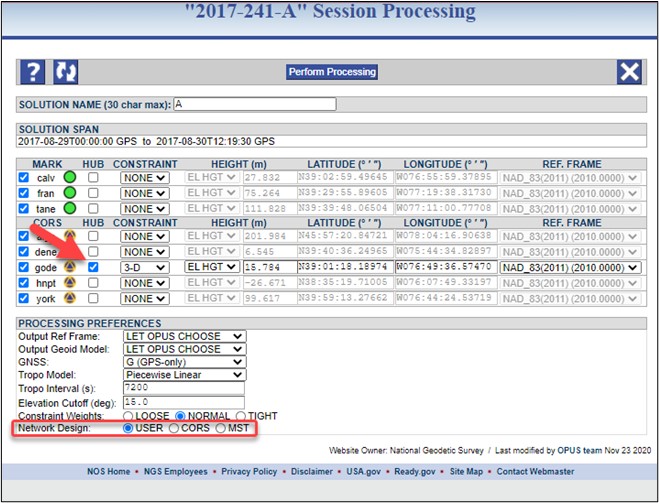
Fig. 11.3 Example session processing page noting the one hub constrained 3D under “User” selected network design
USER: The default (and design recommended for submission to NGS) is “USER”, an example is shown in Fig. 11.4. OP attempts to choose the best hub from the list of CORSs selected for the project. This is typically the closest and/or most centrally located CORS with respect to the user marks. If OP does not select a hub, or if the user disagrees with the hub selection, a new hub will have to be chosen manually. As mentioned in Section 8, certain larger projects may require multiple hubs if user marks are separated by 500 km or more. If multiple hubs are necessary, then each sessions hub must connect to all other hubs. In other words, each hub should be present in all sessions. Note that a hub can also be an active (non-CORS) station if it has 24-hour data files.
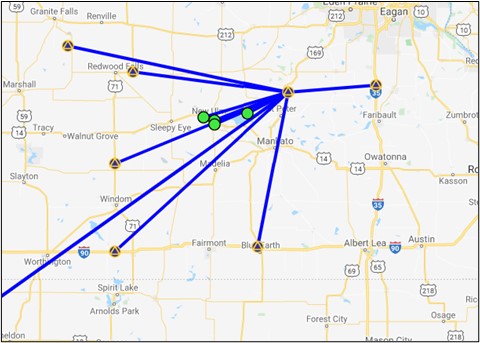
Fig. 11.4 Map showing an example of the USER/”hub-and-spoke” network design
Caution
For submission to NGS for publication, NGS recommends a “hub” design that keeps baselines to a maximum of 250 km in length. For most projects, that will mean selecting one hub. For larger area projects, multiple hubs might be necessary
CORS: The CORS Network Design strategy automatically selects all included CORS as hubs, as shown in Fig. 11.5. Note that this is not an acceptable design for submission to NGS.
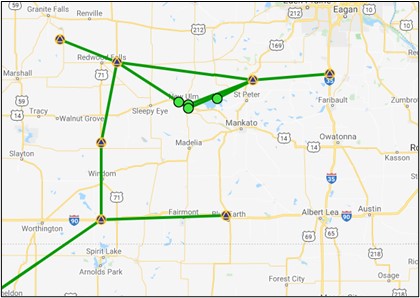
Fig. 11.5 Map showing an example of a “CORS” network design
MST: A Minimal Spanning Tree (MST) connects all the user marks and CORS together seeking the fewest and shortest possible unique baselines, an example is shown in Fig. 11.6. All user marks and CORS are designated as hubs. Note that this is not an acceptable design for submission to NGS.
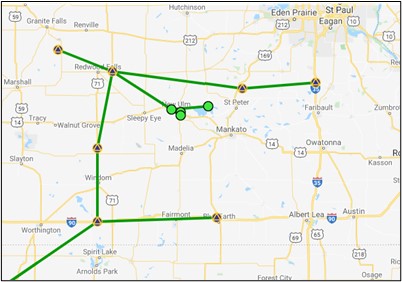
Fig. 11.6 Manage Map showing an example of a “MST” network design
Caution
For any selected design, there is a limit of 99 marks including CORSs/IGS stations per session