Leveling and Vertical Networks
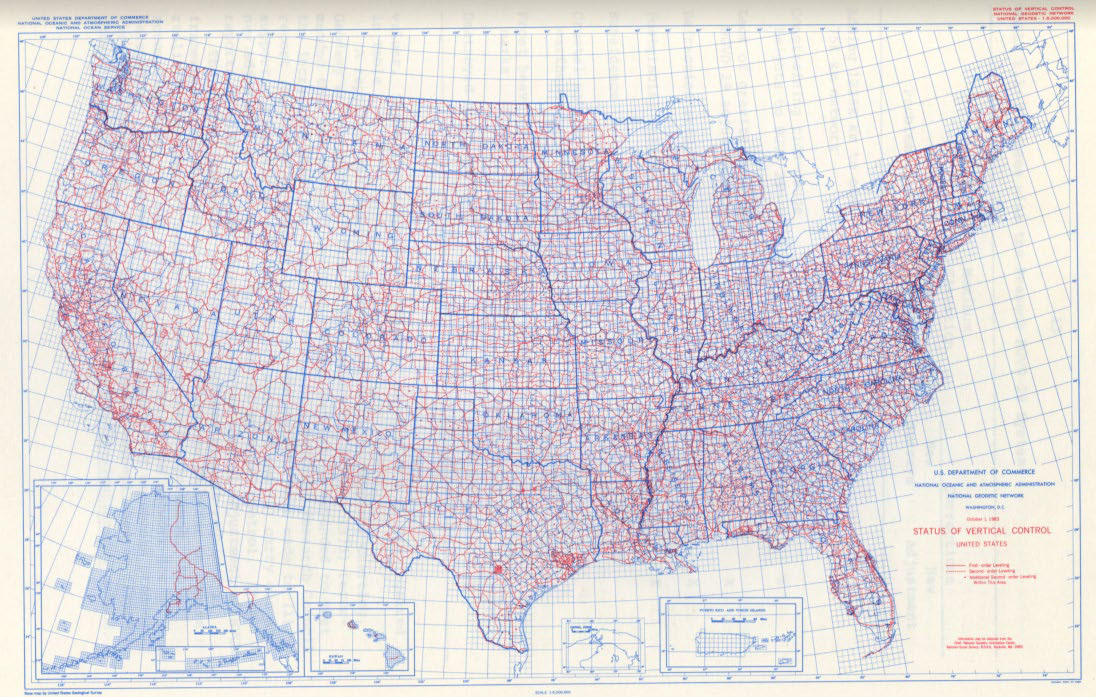
This was the status of vertical control in the United States, October, 1, 1983.
As far back as 1817, the Survey of the Coast began determining elevations in coastal areas using trigonometric methods. Over time, the trigonometric methods were replaced by a more accurate process called “spirit leveling.” Leveling involves determining differences in elevation between survey points following a “leap frog” approach.
The first geodetic leveling was along the Hudson River in 1856. Similar to the Transcontinental Arc of Triangulation, a leveling campaign was planned to cross the country along the 39th parallel or degree of latitude. Since then, many leveling projects have been conducted all across the U.S. and the results mathematically adjusted into one vertical network.
Additionally, re-leveling campaigns have revealed areas where benchmarks had been moved due to earthquakes, postglacial uplift, and subsidence due to the withdrawal of underground resources such as water and oil.